Introduction to QBASIC
QBASIC stands Quick Beginners All purpose Symbolic Instruction Code which is a popular high level language for beginners developed by Microsoft corporation originally developed by Thomas Kurtz and John Kemeny. It is very easy to use and understand so, It is popular among students.
Features of QBASIC
- It use simple English like structure.
- It has user friendly interface.
- It automatically checks syntax error.
- It has wide range keywords.
- We can use both mouse and keyboard on its interface.
- It capitalize keyword automatically.
Data types used in QBASIC
Numeric data: It consist of numeric values i.e. numbers 0-9 and its combination. For eg; 45,12,1
String data: It consist of alphanumeric value i.e combination of letters and numbers. For eg; “global” , “pokhara7”
Variables: Those entities which holds either numeric or alphanumeric (string) values and changes its value throughout the time of program execution is called variables. There are two types of variables.
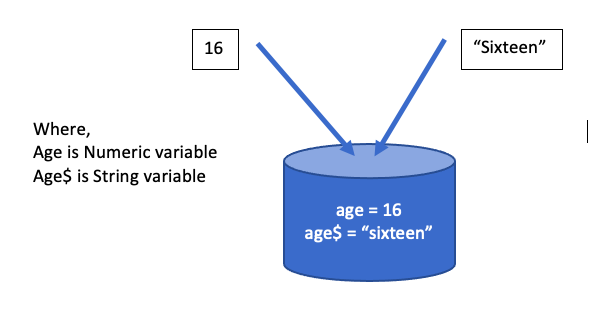
Numeric variable: Those entities which holds only numeric values and changes its value throughout the time of program execution is called numeric variables.
Eg, age = 17, i =2 , wardno = 12
String variable: Those entities which holds only alphanumeric values and changes its value throughout the time of program execution is called string variables.
Note: String variable should end with ‘$’ sign and its respective value should be enclosed within double quotation “ “.
Example: school$ = “global”, fname$ = “Krishna” , address$ = “Pokhara”
Rules while writing variables name:
- Variable name should be 1 to 40 character long.
- Blank space in variable name is not allowed.
For eg, ward no = 12 (Invalid) , wardno = 12(valid)
School name$ = “global” (Invalid)
Schoolname$ = “global” (Valid)
3. Any special symbol except $, #, !, %, & symbols are not allowed in variable name.
Ward*no = 13 (Invalid) , ward$no = 14 (invalid)
4. Keyword cannot be used as a variable name.
Print =3 (Invalid)
Cls =8 (Invalid)
Name =4 (invalid) if,else,while,for
5. Variable name should not start with number.
123abc = 2 (invalid), abc123 =2 (valid)
123fname$ = “global” (invalid)
fname123$ = “global” (valid)
Constant: Those entities which holds either numeric or alphanumeric (string) values and doesn’t changes its value throughout the time of program execution is called constant. There are two types of constant.
Numeric constant: Those entities which holds only numeric values and doesn’t changes its value throughout the time of program execution is called numeric constant.
Eg, age = 17, i =2 , wardno = 12
String constant: Those entities which holds only alphanumeric values and doesn’t changes its value throughout the time of program execution is called string constant.
Note: String variable should end with ‘$’ sign and its respective value should be enclosed within double quotation “ “.
Example: school$ = “global”, fname$ = “Krishna” , address$ = “Pokhara”
Operators: The special sign or symbol that we use in our program to perform some specific functions or operation are known as operators. Types of operators:
Arithmetic operators: It performs mathematical calculations
+ , – , * , / , \ , MOD, ^
5+2 =7
5/2=2.5 (exact division)
5\2 =2 (integer division)
5 MOD 2 = 1 (Modulus division)
5^2 = 25
Relational operator: It helps to compare different operands
>, <, >= , <= ,= , <> (not equal to)
Logical operator: It helps to make logical comparison.
AND, OR, NOT
String operators: It helps to add two or more string. The process of adding two or more string is known as string concatenation.
+
C$ = a$+b$
QABSIC Expression
a=r2. → a=r^2
a=l.b → a =l*b
i = (p*t*r)/100


1 comment
Serving Iraq with pride, BWER supplies high-performance weighbridges designed to improve transport logistics, reduce inaccuracies, and optimize industrial processes across all sectors.